Melanoma Skin Cancer
Melanoma is the most severe form of skin cancer, and it originates in the melanin cells in the skin. While scientists are still unclear regarding the exact causes of melanoma, studies have shown that exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays increase the risk of developing this form of skin cancer. As such, areas of the body that are frequently exposed to the sun (i.e. legs, back, arms, neck) tend to be at a higher risk of developing Melanoma.
What are the risk factors?
The best way to avoid skin cancer is to practice good preventative measures. Appropriate sun wear as well as appropriate sunblock can help to reduce the risk of developing skin cancer. In some cases, however, this cancer may develop in areas that are not frequently exposed to the sun, such as the heels and/or abdomen. The following conditions may put you at a greater risk of developing melanoma:
- Age – Skin cancer tends to develop slowly, which helps to explain why older individuals have a higher risk of developing skin cancer than younger people. However, this does not exclude younger people from developing skin cancer. Appropriate sun safety will significantly reduce the possibility of certain skin cancers.
- Fat Cells – A recent study showed that liposuction in overweight mice helped to reduce the instance of skin cancer. Studies regarding this finding in humans are currently ongoing.
- Fair Skin – Individuals with fairer skin do not have the necessary protection from the sun that melanin provides.
- Frequent history of sunburns – Ultraviolet (UV) radiation damages the skin leading to sun burns. The skin will try to correct the damage, but individuals who have received severe sunburns multiple times put themselves at greater risk of developing skin cancer.
- History of Skin Cancer – If you or a member of your family have previously developed skin cancer, this may put you at higher risk.
- Immuno-suppressed – If you have a weakened immune system, whether from sickness (HIV/AIDS, Leukemia) or from medication, you may be at a higher risk of developing skin cancer.
- Moles – If you develop moles and/or freckles easily you may be at higher risk of developing skin cancer. Click here to learn more about moles and skin cancer.
- Overexposure to UV rays – Spending excessive amounts of time in the sun and/or tanning (i.e. tanning beds/lamps) may make you significantly more likely to develop skin cancer. This is especially true for individuals who live at higher altitudes and/or sunny climates.
How can I tell if I have skin cancer?
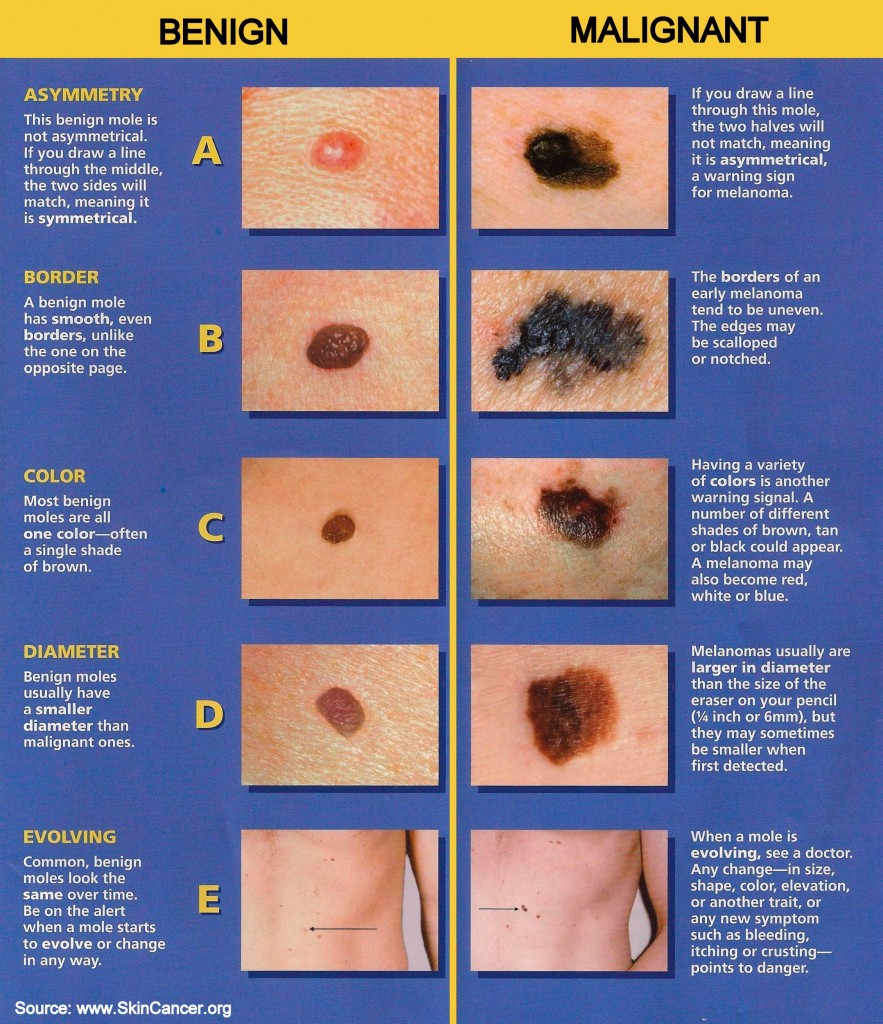 Dr. Ghohestani recommends the ABCDE rule for early skin cancer detection. This rule and its particulars can be found by clicking here. The biggest key to remember with Skin Cancer, or any other cancer, is that early detection is often the greatest predictor in treatment possibility. The sooner the cancer is diagnosed, the higher probability of treatment success. Click the picture to the right to see a larger version of the ABCDE guidelines provided by the Skin Cancer Foundation. If you feel you might have skin cancer, call us immediately to set up a skin check.
Dr. Ghohestani recommends the ABCDE rule for early skin cancer detection. This rule and its particulars can be found by clicking here. The biggest key to remember with Skin Cancer, or any other cancer, is that early detection is often the greatest predictor in treatment possibility. The sooner the cancer is diagnosed, the higher probability of treatment success. Click the picture to the right to see a larger version of the ABCDE guidelines provided by the Skin Cancer Foundation. If you feel you might have skin cancer, call us immediately to set up a skin check.
What are my treatment options?
The best treatment option for skin cancer is prevention. Avoiding exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation significantly reduces the risk of developing skin cancer. Additionally, frequent skin checks are advised in order to monitor moles and other potentially risky lesions on your skin.
For those who have developed skin cancer, treatment will vary depending on the type and extent to which the cancer has spread. The following treatment options are some of the most common for those with skin cancer:
- Freezing – Certain types of Actinic Keratosis and early-stage skin cancers can be treated through cryosurgery (freezing cancerous cells with liquid nitrogen).
- Lasers – For certain superficial cancers, a laser treatment helps to vaporize growths while reducing exposure to surrounding skin. This approach may lead to less downtime, smaller scars, and less swelling.
- Mohs Surgery – Physicians will generally use this approach for cancers that are larger and/or recurring and may be more difficult to treat. The Mohs Surgery is a process where the physician cuts out the cancerous lesions layer by layer and examines each slice under a microscope. This process continues until no cancerous tissue is evident under the microscope. The goal of this process is to remove cancerous cells without affecting surrounding healthy cells.
- Radiation and/or Chemotherapy – In cases where surgery is not an option, radiation and/or chemotherapy may be the better approach. Systematic chemotherapy may be used when skin cancer is advanced to the point where it has spread to other organs in the body.
- Surgery – The doctor will excise the cancerous lesion and some surrounding healthy skin to reduce the probability of recurrence. In some instances, the physician will also use a curet (circular blade) to scrape off cancerous cells. This process may be followed by electrodesiccation, which is an electric needle used to destroy remaining cancerous cells.
******
Why choose the Texas Institute of Dermatology for your melanoma treatments?
Our mission is to serve as a leading center for understanding and treating skin, hair, and nail diseases in South Texas through excellence in patient care, research, and education. We want you to feel that you have been treated with the comfort, privacy, safety, and satisfaction that you deserve. This is why all of our procedures are performed or supervised by our renowned dermatologist, Dr. Reza Ghohestani. His experience, combined with the latest technology and a caring staff, is why the Institute is consistently ranked among the top dermatology centers in San Antonio and Boerne areas based on satisfaction surveys. We currently serve communities throughout Bexar and Kendall counties, including San Antonio, Boerne, Leon Springs, Fair Oaks Rank, Canyon Lake City, etc. Many of our patients also come from San Marcos, New Braunfels, Kerrville, Austin, Wimberly, and Corpus Christi.
* If the Content contained on this site contains medical or health sciences information, it is intended for answering some common skin care questions. No suggested test or procedure should be carried out without visiting a health care professional and unless, in the reader’s judgment, its risk is justified. Because of rapid advances in the medical sciences, we recommend that the independent verification of diagnoses and drug dosages should be made. NEITHER TEXAS DERMATOLOGY INSTITUTE NOR ANY OF ITS AFFILIATES OR LICENSORS SHALL BE LIABLE TO YOU OR ANYONE ELSE FOR ANY LOSS OR INJURY, CAUSED IN WHOLE OR PART BY ITS NEGLIGENCE OR CONTINGENCIES BEYOND ITS CONTROL IN PROCURING, COMPILING, INTERPRETING, REPORTING OR DELIVERING INFORMATION THROUGH THE SITE. IN NO EVENT WILL TEXAS DERMATOLOGY INSTITUTE, ITS AFFILIATES OR LICENSORS BE LIABLE TO YOU OR ANYONE ELSE FOR ANY DECISION MADE OR ACTION TAKEN BY YOU IN RELIANCE ON SUCH INFORMATION. TEXAS DERMATOLOGY INSTITUTE AND ITS AFFILIATES AND LICENSORS SHALL NOT BE LIABLE TO YOU OR ANYONE ELSE FOR ANY DAMAGES (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, CONSEQUENTIAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, INDIRECT, OR SIMILAR DAMAGES) EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.You hereby agree to indemnify, defend and hold Texas Dermatology Institute, its directors, officers, shareholders, parents, subsidiaries, affiliates, agents and licensors harmless from and against any and all liability, losses, damages and costs, including, without limitation, reasonable attorneys’ fees, arising from your use of the Site or Content.







